Scientists at St. Jude Youngsters’s Analysis Hospital and the College of Texas Southwestern Medical Middle studied the construction and performance of a transporter concerned in most cancers and immunity. They captured six constructions of the transporter, together with when it was sure to an inhibitor, offering unprecedented perception into the way it works. The findings, printed in Cell, have implications for drug improvement.
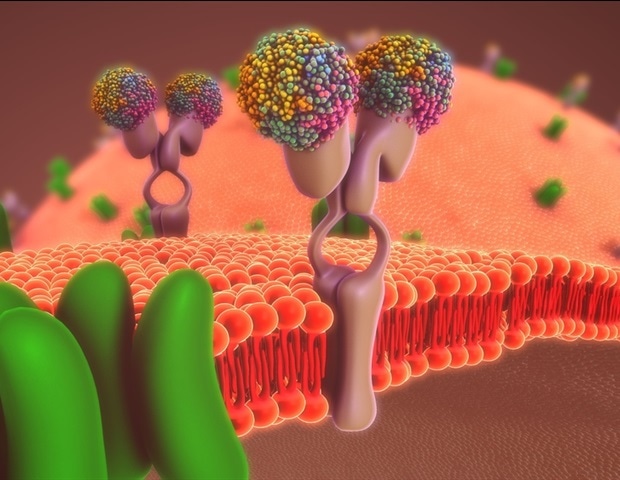
Transporters escort substances throughout the cell membrane in order that they will perform their features. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a crucial signaling molecule that regulates the immune system, blood vessel formation, auditory operate and the integrity of epithelial and endothelial membranes. It aids the development and survival of most cancers cells via chemoresistance and metastasis.
The S1P molecule is synthesized contained in the cell however should cross the cell membrane to hold out its signaling duties. Spinster homolog 2 (Spns2) is an S1P transporter; this protein sits on the membrane and opens towards the within of the cell, binds to S1P, after which opens towards the skin of the cell to launch S1P.
Analysis has proven that altering Spns2 exercise can have therapeutic results in opposition to most cancers, irritation and immune ailments. Nonetheless, the transport mechanism of Spns2 and easy methods to inhibit it was unclear.
We hope our structural data will pave the way in which for the event of improved, extra particular small molecules with larger efficiency in opposition to Spns2 sooner or later. I believe there may be large potential for inhibiting the Spns2 transporter therapeutically.”
Chia-Hsueh Lee, Ph.D., co-corresponding creator, St. Jude Division of Structural Biology
Cryo-EM constructions clarify how the transporter works
The researchers obtained six cryo-Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) constructions of Spns2, together with two functionally related intermediate conformations (shapes) that hyperlink the inward (inside a cell) and outward (exterior the cell) dealing with states. The findings reveal the structural foundation of the S1P transport cycle.
“I believe these outcomes are fairly satisfying as a result of capturing a specific transporter’s main conformations is uncommon,” Lee added. “By evaluating these totally different constructions, now we have a really detailed image of how this transporter captures the S1P signaling molecule.”
“We used cryo-EM to seize the construction of this transporter and uncover the way it strikes S1P to the skin of the cells,” mentioned co-first creator Shahbaz Ahmed, Ph.D., St. Jude Division of Structural Biology. “We additionally studied an inhibitor and supplied the structural information for the way it binds the transporter and blocks its exercise.”
The researchers studied how Spns2 binds to the inhibitor 16d, a selected small molecule that has demonstrated only a few off-target results. The researchers discovered that 16d stops transport exercise by locking Spns2 within the inward-facing state. The work aids the event of superior Spns2 inhibitors.
“This inhibitor really blocks the protein in an inward conformation. When the protein is blocked, it can not transition from inward to outward-facing, and it can not throw the signaling molecule from inside to exterior the cells,” Lee mentioned. “As well as, the inhibitor bodily blocks the binding of the signaling molecule as a result of they each bind to the identical cavity.”
Cell floor molecules are a lovely goal for drug improvement. G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a kind of cell floor protein that’s the goal of one-third of all Meals and Drug Administration-approved therapeutics. As cell floor molecules, transporters might have comparable potential for drug improvement. Due to this fact, understanding their construction and performance has the potential to make vital inroads for enhancing illness therapy.
“Our work reveals the atomic particulars of the Spns2-mediated S1P transport cycle, which is vital to understanding how this signaling sphingolipid circulates in our immune system,” mentioned co-corresponding creator Xiaochun Li, Ph.D., Departments of Molecular Genetics and Biophysics, College of Texas Southwestern Medical Middle. “The constructions additionally assist the event of potent Spns2 inhibitors, which can contribute to most cancers and autoimmune illness therapy.”
Authors and funding
The research’s different first authors are Hongwen Chen, College of Texas Southwestern Medical Middle, and Hongtu Zhao, St. Jude. Different authors are Nadia Elghobashi-Meinhardt, Technical College Berlin; Jae Hun Kim and Jeffrey McDonald, College of Texas Southwestern Medical Middle; and Yaxin Dai, St. Jude.
The research was supported by grants from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (P01HL160487, 1P30DK127984, R01GM134343 and R01GM143282), the Welch Basis (I-1957), the Damon Runyon Most cancers Analysis Basis (DRR-53S-19) and ALSAC, the fundraising and consciousness group of St. Jude.
Supply:
Journal reference:
Chen, H., et al. (2023) Structural and Practical insights into Spns2-mediated transport of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Cell. .