The rise in excessive throughput sequencing applied sciences has broadened the identified range of the virosphere. These applied sciences have enhanced the frequency and accuracy of viral surveillance. In an Amazonian metropolitan area, scientists have been finding out the viral communities related to the human-animal interface. Now, a latest research within the journal targeted on the identification of a novel rodent-borne arterivirus.
Examine: . Picture Credit score: streetflash / Shutterstock
Background
The Worldwide Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) has regarded as an necessary supply of organic info, which is used for viral classification. Because the 2014 ICTV launch, the Arteriviridae household of order Nidovirales has exhibited a six-fold enhance in species content material. At current, this household contains 13 genera, 11 subgenera, and 23 species. Amongst these, the Variarterivirinae and Heroarterivirinae subfamilies have been related to rodents.
Viruses belonging to the Arteriviridae household have been characterised as spherical, enveloped, single-stranded, and positive-sense multi-cistron RNA genomes. Within the context of their genomic group, a marginal variation within the open studying body (ORF) was noticed amongst all species belonging to the Arteriviridae household. Conserved domains have been recognized that embrace ORFs 1a (3C-like protease-3CLpro) and 1b (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase-RdRp). These are normal markers for genetic distance indexes and phylogenetic inferences used for taxonomic differentiation inside the household.
Non-human mammalian viruses inside wide-ranging hosts, comparable to rodents, shrews, horses, hedgehogs, and possums, which have but not been assigned to any species, are generally known as arterivirids. Nearly all of arteriviruses, comparable to simian hemorrhagic fever virus (SHFV) and equine arteritis virus (EAV), are pathogens of veterinary significance. Nevertheless, lactate dehydrogenase elevating virus (LDV), which belongs to the Arteriviridae household, infect mice.
Most just lately described rodent arteriviruses have African, Asian, or European origins. These viruses had been recognized from samples collected from Ukraine, China, Cameroon, Mozambique, and Tanzania by metagenomic research.
In regards to the Examine
The present research is an element of a big surveillance research to discover the viral communities related to wild mammals on the human–animal interface. Tissue samples had been collected from wild mammals in Santa Bárbara do Pará, Brazil. For this research, animals had been captured utilizing Tomahawk and Sherman traps in forest areas with shut human habitations and agricultural practices. A complete of 39 mammals, 12 rodents, 18 marsupials, and 9 chiropterans had been captured.
Blood and serum samples had been collected from the captured animals. These animals had been then anesthetized and euthanized. Subsequently, tissue samples from lymph nodes, spleen, coronary heart, and lungs, had been collected. Tissue samples of rodents had been pooled and analyzed. Oecomys sp. was recognized from rodents primarily based on morphological traits. The rodents didn’t current any obvious indicators of sickness.
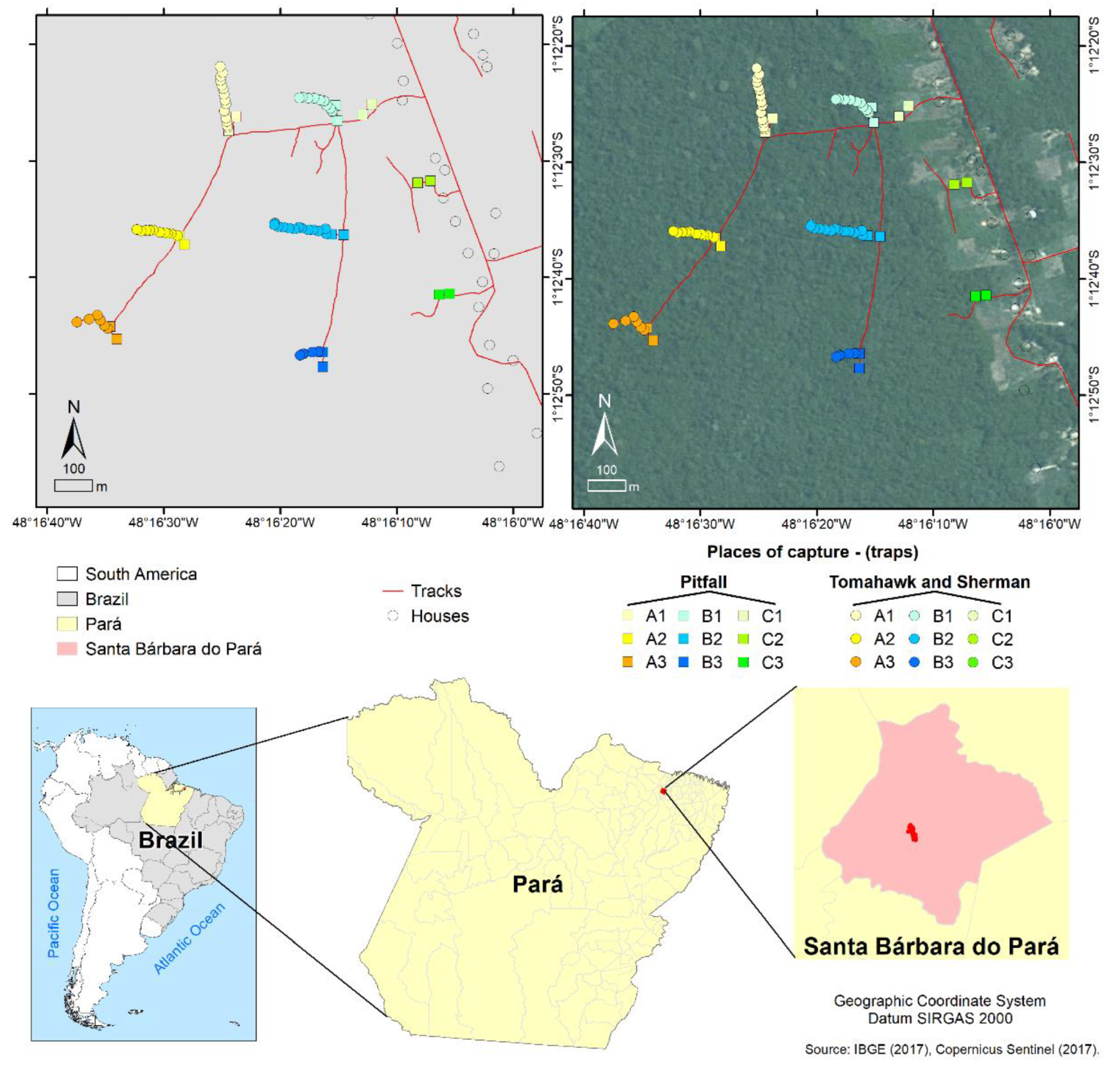 Map of the gathering space within the Expedito Ribeiro village in Santa Bárbara do Pará municipality (Pará state, Brazil) and its location within the Brazilian territory. Traps had been positioned within the open subject surrounding the human habitations (A1–A3), the forest fragment border (B1–B3), and its most inside area (C1–C3). The IBGE (2017) and Copernicus Sentinel (2017) databases had been consulted to organize the maps.
Map of the gathering space within the Expedito Ribeiro village in Santa Bárbara do Pará municipality (Pará state, Brazil) and its location within the Brazilian territory. Traps had been positioned within the open subject surrounding the human habitations (A1–A3), the forest fragment border (B1–B3), and its most inside area (C1–C3). The IBGE (2017) and Copernicus Sentinel (2017) databases had been consulted to organize the maps.
Examine Findings
An nearly full genome was retrieved, which contained 4 remaining contigs associated to identified arterivirids. The genomic sequence revealed that the virus was a member of the Arteriviridae household.
ORF1a and ORF1b, that are the 2 most distinguished ORFs of arterivirid genomes, had been recognized. ORFs expressing the non-structural proteins (NSPs) and structural proteins (envelope (E), glycoproteins (GP2 to GP5), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) had been detected. InterProScan search was used to detect three cysteine-protease domains of NSP1 and NSP2, attribute of arteriviruses, within the predicted sequence of polyprotein 1a.
The whole mitochondrial genome of the host was recovered, which confirmed a 99.38% similarity with Oecomys paricola. This virus was tentatively named after the host genus, Oecomys arterivirus 1 (OAV-1). Within the phylogenetic evaluation, this novel arterivirus was positioned with a excessive help bootstrap worth on the most basal department within the clade of porcine and rodent arterivirids. This corresponded to the Variarterivirinae subfamily clade, essentially the most proximal taxon.
Despite the fact that the imply distance between OAV-1 and members of the Variarterivirinae subfamily barely exceeds the utmost intragroup distance for the subfamily, this taxon is most associated to the virus. The space values between OAV-1 and the Variarterivirins are completely out of the intergroup vary.
This research revealed that OAV-1 is extremely divergent on each amino acid and nucleotide ranges, which indicated that it may very well be part of a definite clade of arteriviruses. This clade may very well be unique to the area. Based mostly on distance evaluation, this virus is a divergent illustration of a brand new genus within the Variarterivirinae subfamily.
Conclusions
The invention of novel arteriviruses could problem the present taxonomic classification. Though arteriviruses are non-human viruses, their significance as wildlife and livestock pathogens should not be uncared for. The Brazilian arboreal rice rat, Oecomys paricola, was recognized because the host of OAV-1. Because the elevated contact between home and wild species favors viral spillover, additional surveillance research are required to uncover the variety and coevolutionary patterns of the Arteriviridae household within the Amazon.
usechatgpt init success
